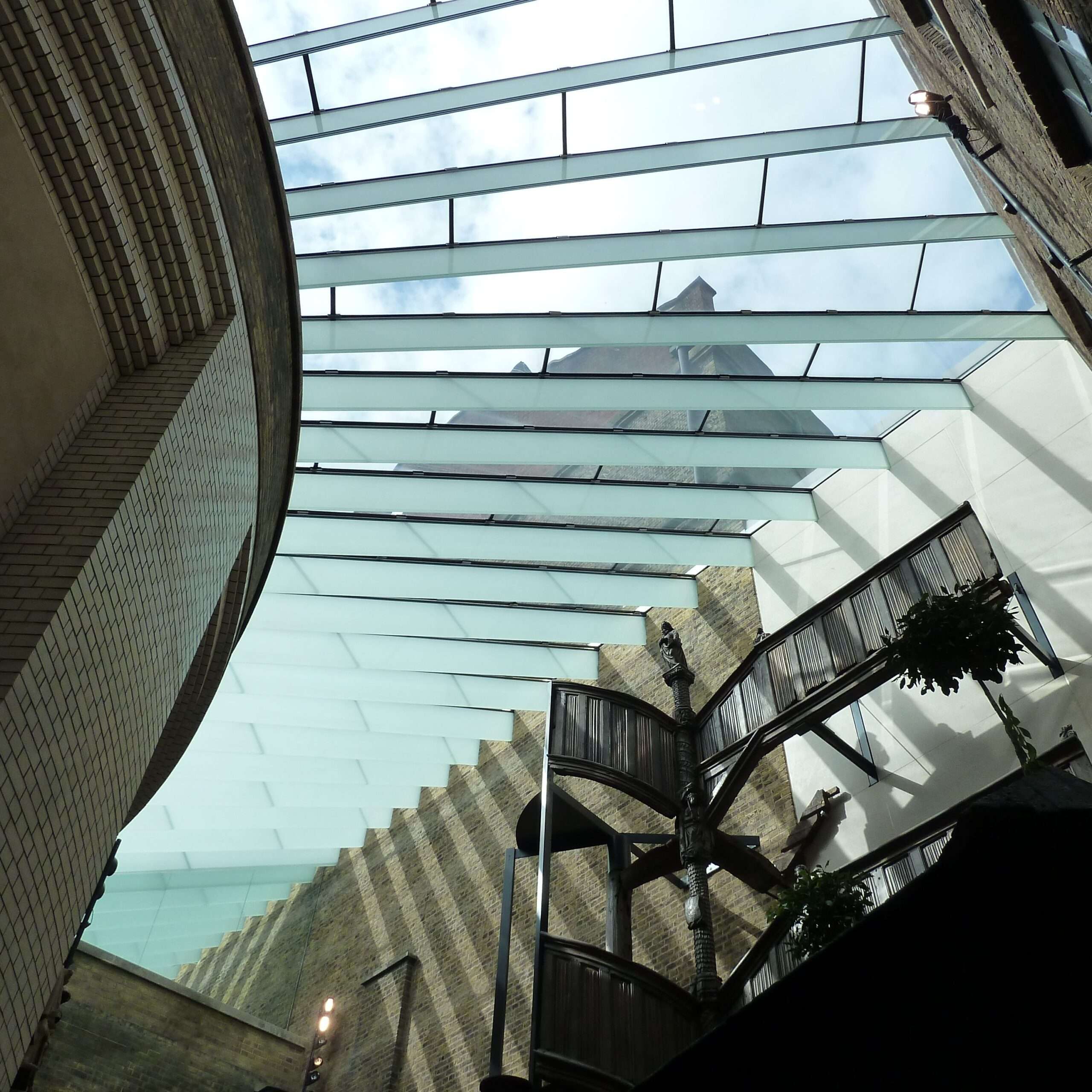
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass that holds together when shattered. In the event of breaking, it is held in place by an interlayer, typically of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), between its two or more layers of glass. Laminated glass applications. Skylight glazing, glass balustrades, glass floors and automobile windshields typically use laminated glass.
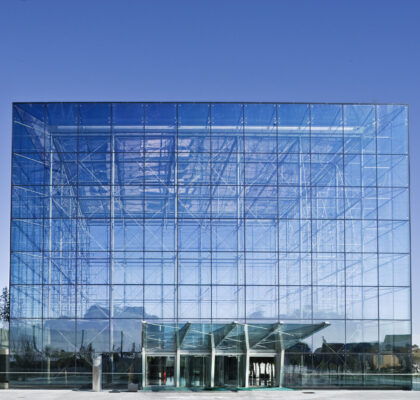

Advantages:
- The interlayer keeps the layers of glass bonded even when broken, and its high strength prevents the glass from breaking up into large sharp pieces.
- Laminated glass is also used to increase the sound insulation rating of a window, where it significantly improves sound attenuation compared to unlaminated single glass panes of the same thickness.
- An additional property of laminated glass for windows is that a PVB and EVA interlayer can block essentially most ultraviolet radiation.